In the digital era, where a strong online presence is crucial for success, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a pivotal role. Among various SEO strategies, a sitemap is a fundamental element that can significantly improve your website’s visibility and indexing on search engines. This article delves into the process of setting up a sitemap in Google Search Console, explaining its importance and providing a step-by-step guide to optimize your website for better search engine rankings.
Understanding Sitemaps
A sitemap is essentially a roadmap of your website, containing links to all the important pages. It aids search engines like Google in discovering, crawling, and indexing your site more efficiently. Sitemaps are particularly beneficial for larger websites, websites with a significant amount of content, or those that frequently update their content.
Types of Sitemaps
There are two primary types of sitemaps: XML and HTML. Let’s take a closer look at them.
XML Sitemaps
XML (Extensible Markup Language) sitemaps are designed specifically for search engines. They act as a guide, helping search engines like Google discover and crawl the pages on your website. An XML sitemap is a structured file that lists all the important URLs of your site, along with additional information such as the last modification date, the frequency of changes, and the priority of different pages in relation to one another.
Key Features of XML Sitemaps:
- Machine-readable format: XML sitemaps are structured in a way that is easily processed by search engines.
- Includes metadata: Alongside URLs, XML sitemaps can provide metadata about each page, such as how often it’s updated and its relative importance.
- Support for large websites: XML sitemaps are particularly beneficial for large websites or websites with a significant amount of new or updated content.
HTML Sitemaps
HTML sitemaps are created for the convenience of website visitors, allowing them to navigate and find content on your site easily. Unlike XML sitemaps, which are intended for search engines, HTML sitemaps are user-friendly and designed to enhance the user experience. They are typically a single webpage that includes a structured list of links to various sections and pages of your website.
Key Features of HTML Sitemaps:
- User-friendly layout: HTML sitemaps are designed to be easily readable and navigable by humans.
- Enhances site navigation: They provide a clear overview of the website’s structure, helping users find information quickly.
- Accessibility: HTML sitemaps can be particularly helpful for larger websites or for users who prefer a more traditional method of browsing.
Importance for SEO and User Experience
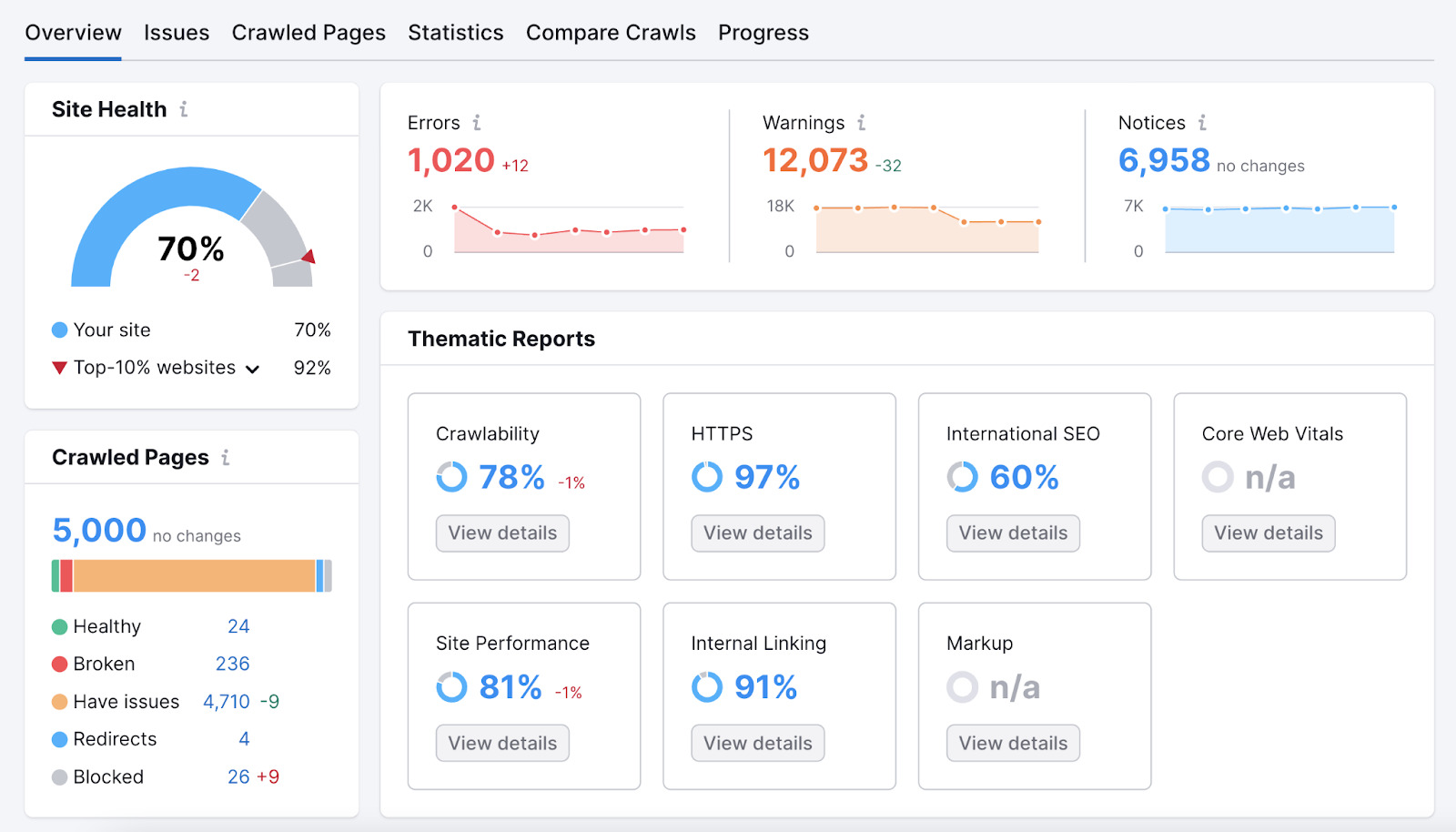
XML sitemaps are vital for SEO as they facilitate faster and more efficient indexing of your website by search engines. By providing a clear structure of your site’s content, they ensure that search engines don’t miss out on crawling any important pages. While HTML sitemaps may not have as direct an impact on SEO as XML sitemaps, they play a crucial role in enhancing user experience. A well-organized HTML sitemap can improve site navigation, reduce bounce rates, and potentially increase the time users spend on your site.
The Role of Sitemaps in Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool provided by Google that helps website owners monitor and maintain their site’s presence in Google search results. It offers insights into how Google views your site and optimizes its performance in search results.
Before setting up a sitemap in Google Search Console, ensure you have a verified property (your website) in your account. If you haven’t verified your site yet, follow Google’s verification process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Submit a Sitemap
- Create Your Sitemap: Depending on your website’s platform (e.g., WordPress, Shopify), there are different ways to generate an XML sitemap. Many content management systems have built-in tools or plugins for this purpose.
- Locate Your Sitemap URL: Your sitemap URL typically looks like this: http://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml.
- Log in to Google Search Console: Navigate to your property (website) in Google Search Console.
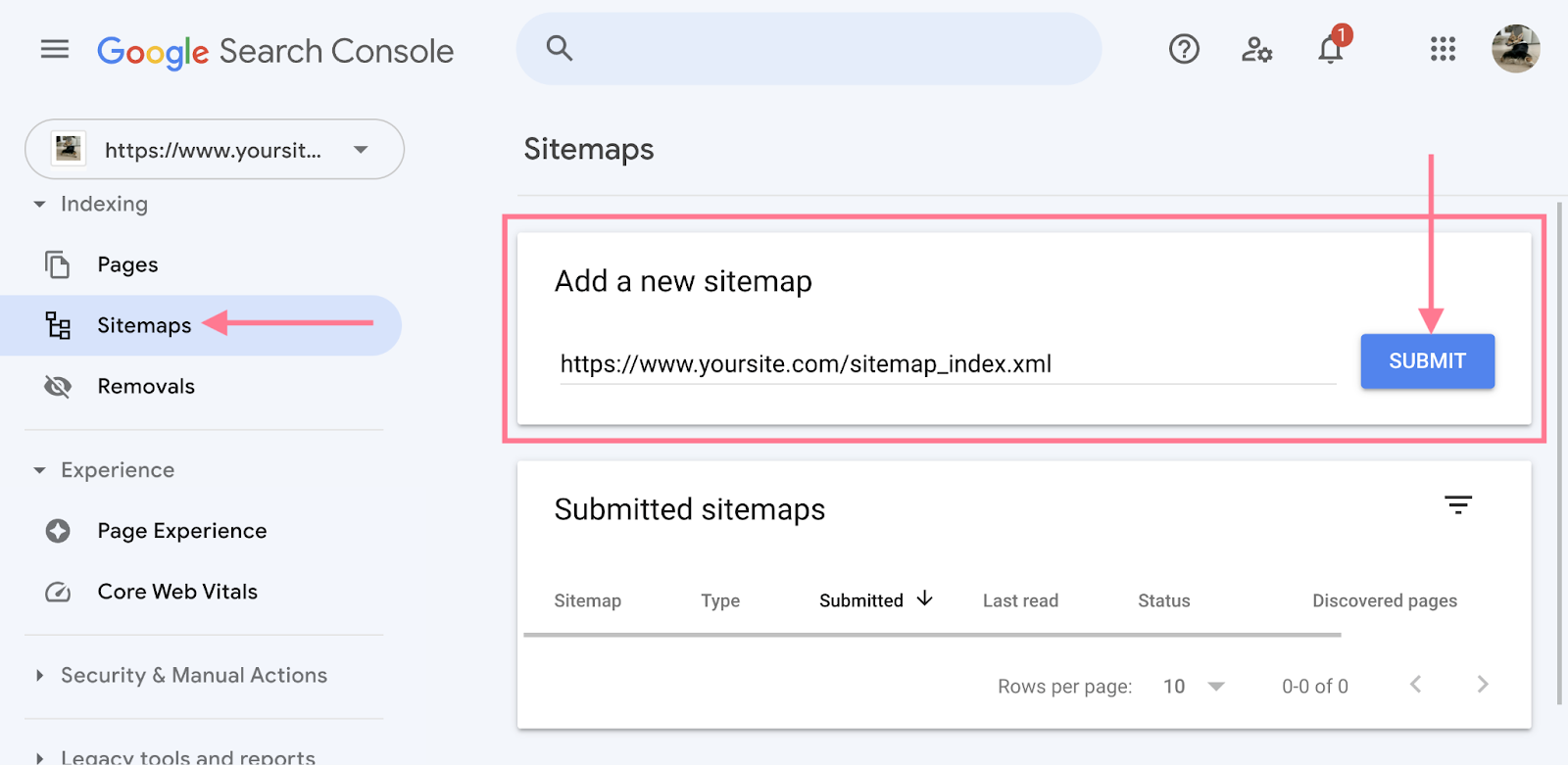
- Submit Your Sitemap: In the Search Console dashboard, find the ‘Sitemaps’ section. Enter your sitemap URL and click ‘Submit’.

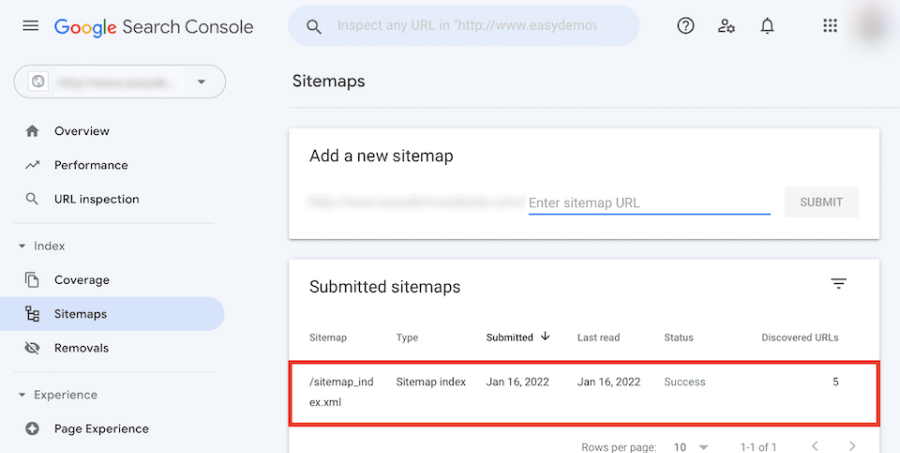
- Monitor the Status: After submission, monitor the status of your sitemap in the Search Console. It will show if your sitemap was successfully processed or if there were any errors.

Best Practices for Sitemap Optimization
- Keep Your Sitemap Updated: Regularly update your sitemap with new pages or changes to existing ones.
- Optimize Your Sitemap Size: For larger websites, consider creating multiple sitemaps or a sitemap index file.
- Prioritize Important Pages: Ensure that your sitemap includes the most important and relevant pages of your website.
- Check for Errors: Regularly monitor your sitemap for any crawl errors and address them promptly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Submitting Outdated Sitemaps: Always ensure your sitemap is current and reflects the latest structure of your site.
- Including Irrelevant URLs: Only include URLs that are important for search engines to crawl.
- Ignoring Sitemap Errors: Failing to address errors in your sitemap can hinder your website’s SEO performance.
Conclusion
Incorporating a sitemap into your SEO strategy is a straightforward yet effective way to enhance your website’s search engine visibility. By following the steps outlined in this article to set up a sitemap in Google Search Console, you can ensure that search engines efficiently crawl and index your website, ultimately driving more organic traffic and improving your online presence. Remember, a well-structured and regularly updated sitemap is a key component of your overall SEO success.