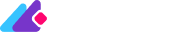Referral traffic, a crucial element in digital marketing, connects users to your website and fosters online growth. In Google Analytics 4 (GA4), understanding referral traffic is essential, especially for those experiencing high referral traffic and conversions.
What is Referral Traffic?
Referral traffic in GA4 refers to visitors arriving at your website through links on other sites not tracked by your GA4 account. New businesses might see less referral traffic due to limited exposure and basic SEO efforts, while established sites and experts often enjoy significant referral traffic through third-party mentions in blogs and videos.
Traffic from direct sources, organic searches, paid ads, social media, and properly tagged email campaigns, as well as traffic from sub-domains or domains set for cross-domain tracking, are not considered referral traffic. Incorrectly grouped referral traffic can skew your data analysis.
Finding GA4 Referral Traffic
Access GA4 referral traffic through Reports → Acquisition → User/Traffic Acquisition Reports. The reports provide session details and information on new users. To find the referral channel, scroll down the tables or use filters and sorting options.

To identify the source websites of referral traffic, switch the dimension to source/medium in the traffic or user acquisition reports. Filtering the table for ‘referral’ entries will reveal the originating websites.
Analyzing Referral Traffic
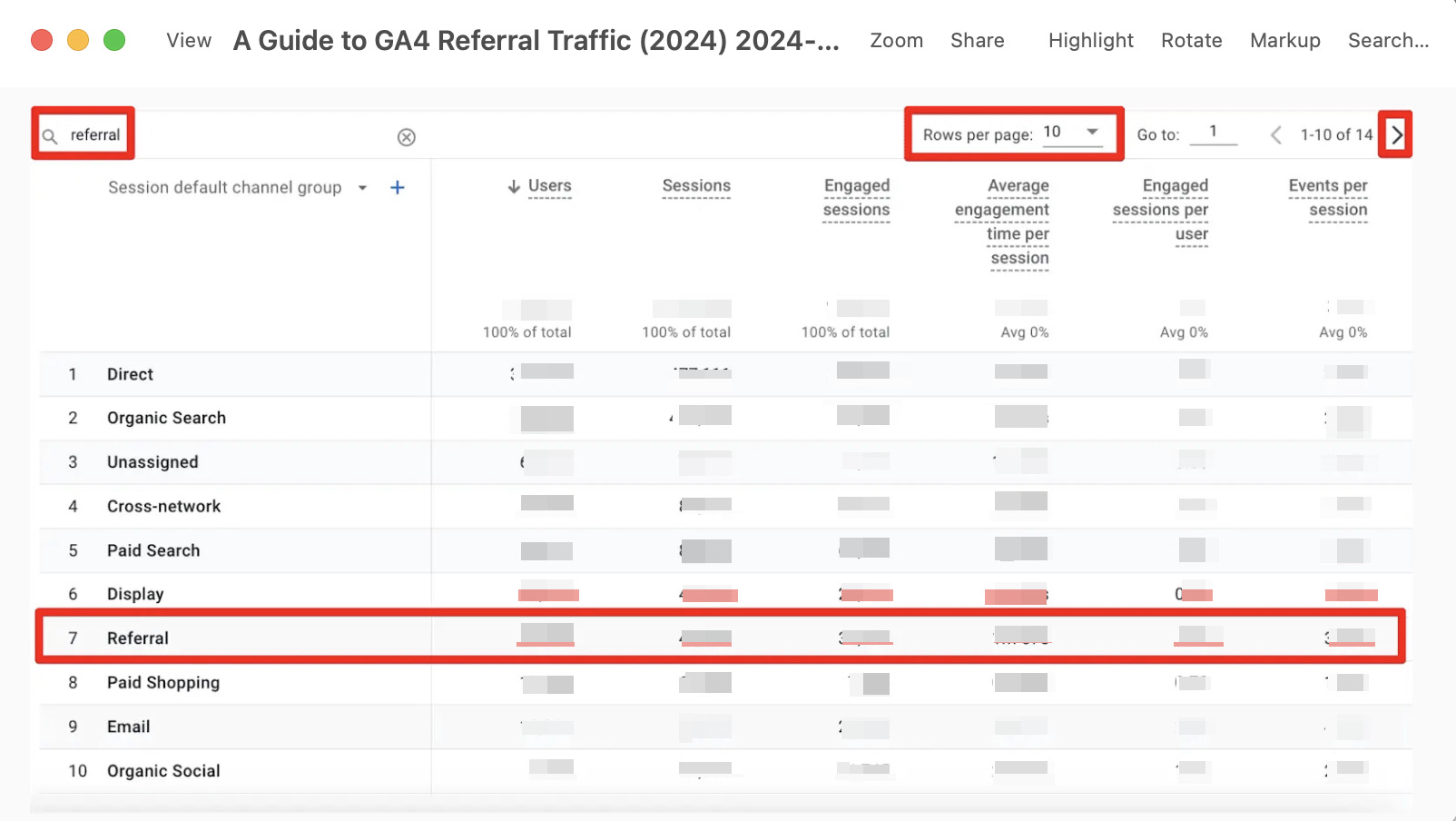
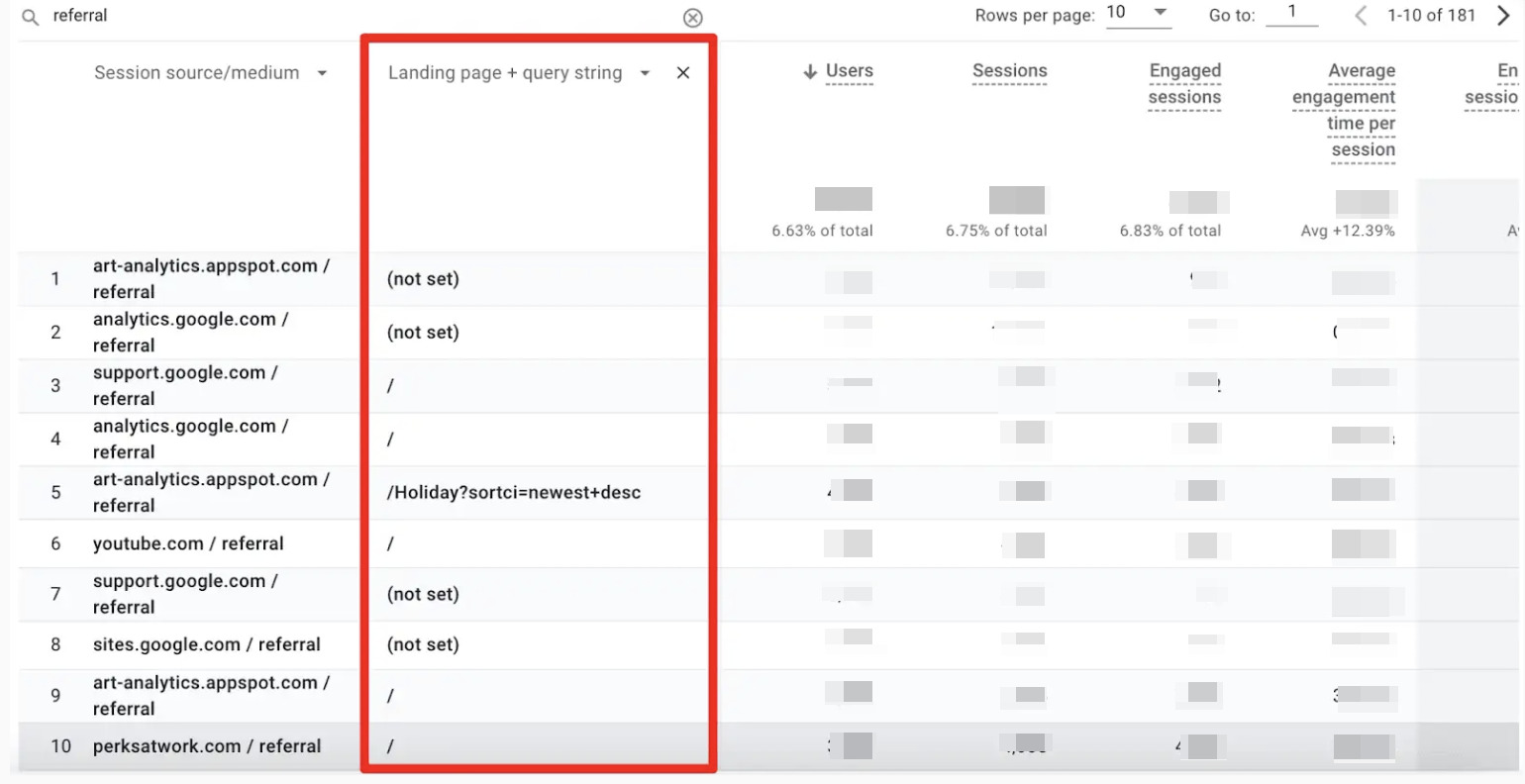
Understanding which pages receive referral traffic and the URLs of the referring pages is vital. In the traffic acquisition report, add a secondary dimension of pages, such as Landing page + query string or Page path and screen class, to determine the landing points of referral traffic.
In summary, effectively managing and analyzing GA4 referral traffic can significantly impact your website’s growth and online presence. It’s crucial to identify, understand, and appropriately utilize this data for strategic decision-making.
Analyzing Specific Referral Sources
To analyze specific referral sources in GA4, add the “Landing page + query string” dimension to the source/medium data. For example, to examine traffic from a specific website, filter the data to see where users are coming from to your site.
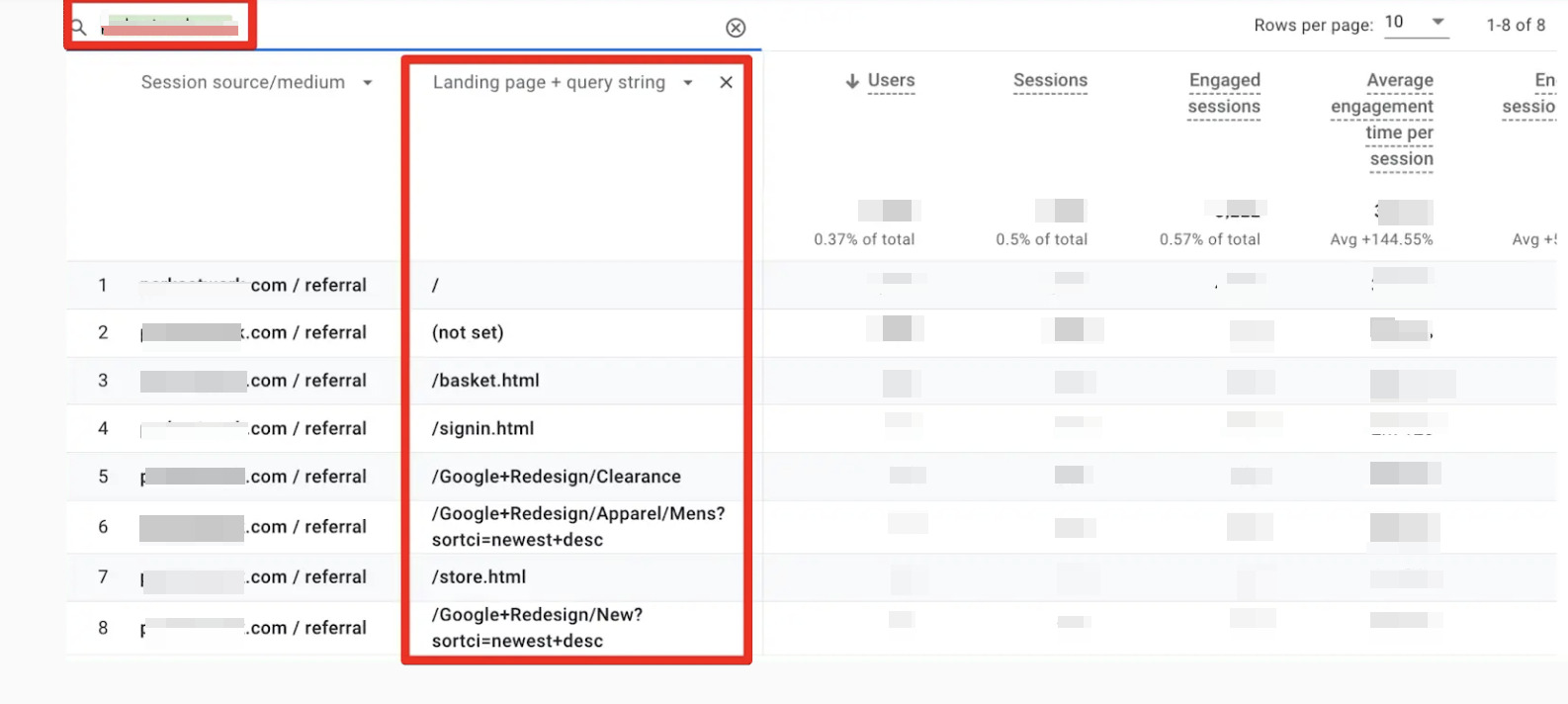
If you are interested in the full URL of a link, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the landing page from GA4.
- Search the landing page text on Google, filtering for the specific referrer site.
- Look for the page with an outbound link to your site to confirm the full URL of the referrer.
- Use browser tools to inspect hyperlink URLs or search for the landing page text in the page’s HTML code.
This method, while not ideal, is useful if you don’t track referrer URLs directly. Alternatively, you can wait for a possible future GA4 update to include this feature, as was available in Universal Analytics (UA).
Excluding Unwanted Referrals
GA4, like Universal Analytics, allows the exclusion of unwanted referral domains. This feature, found under Admin → Data Streams → Configure tag settings, is crucial for accurate traffic analysis.
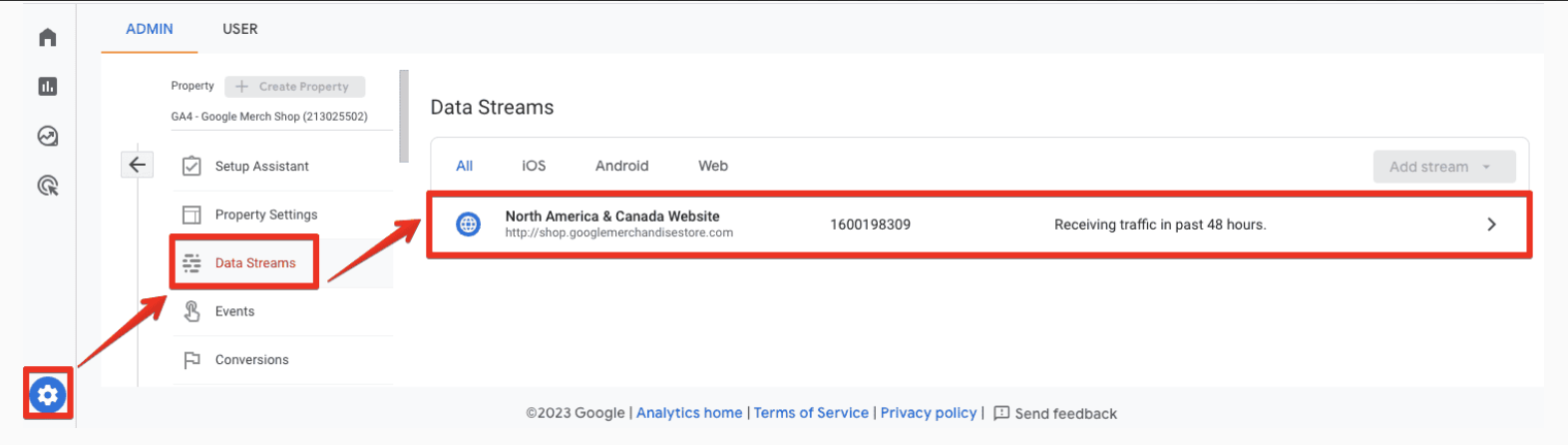
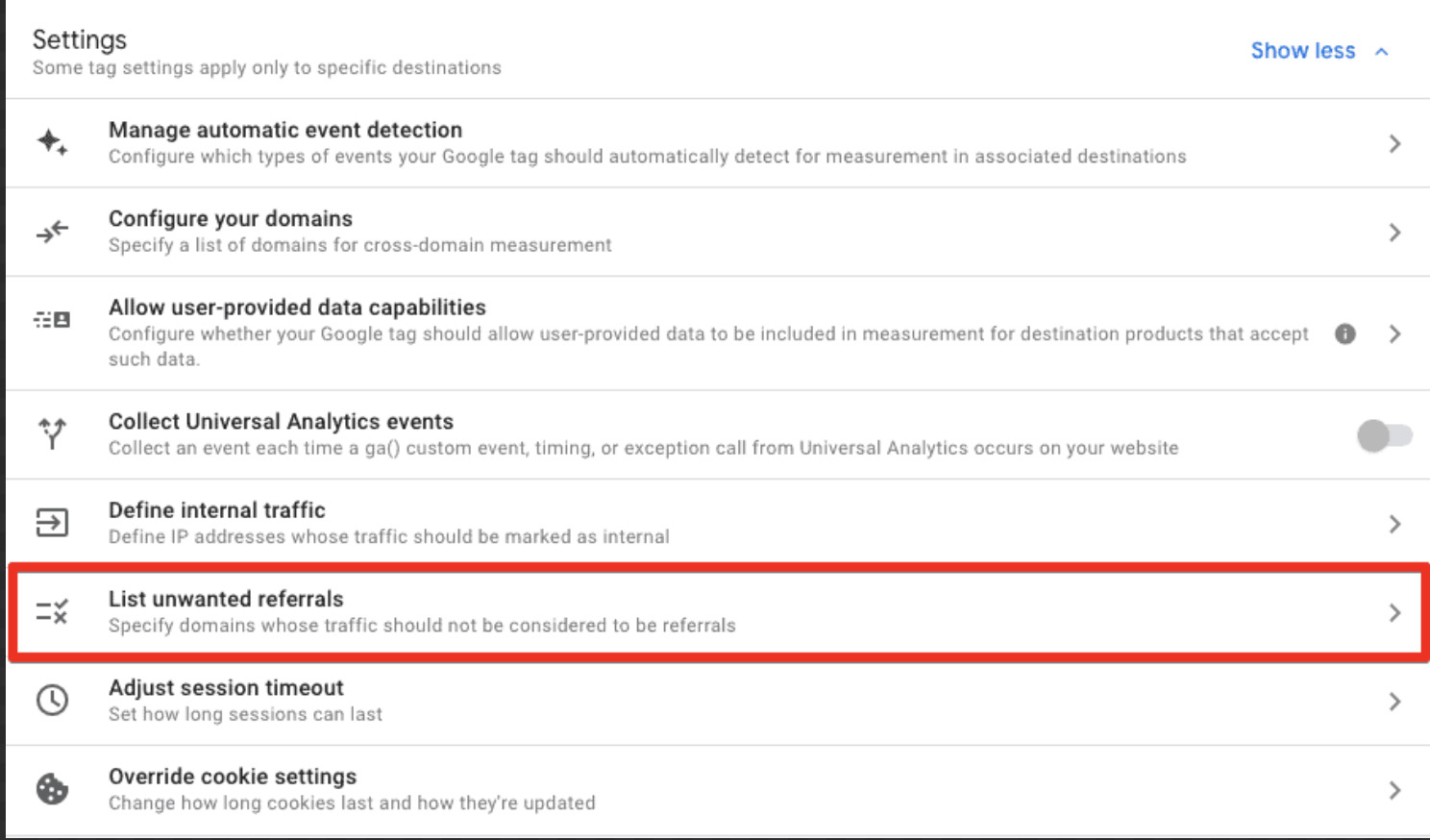
To exclude referrals:
- Access the Google Tag interface in GA4.
- Select “List unwanted referrals” and enter the domains you wish to exclude.
- Choose from five matching conditions (contains, begins with, ends with, exactly matches, matches RegEx).
- Save your changes.
Common unwanted referrals include third-party payment gateways, website-managed interactions (like password recovery emails), and self-referrals. Excluding these ensures that your referral data reflects genuine external traffic sources.
Utilizing Referral Traffic Data
Referral traffic data, often a free source of user acquisition, can be invaluable if effectively analyzed and acted upon. Understanding where your visitors come from, the pages they land on, and the full URLs of the referring sites can inform your marketing strategies and help in optimizing your website for better user engagement and conversions.
In summary, effectively managing and analyzing specific referral sources and excluding unwanted referrals in GA4 can greatly enhance the accuracy and usefulness of your referral traffic data. This allows for more informed decisions in your digital marketing efforts.
Engaging with Referrers
Reaching out to website owners who link to your site can open valuable opportunities. Expressing gratitude for their links can lead to informative discussions about their reasons for linking to your content and potential link-building strategies. This interaction can provide insights for content creation and SEO enhancement.
Evaluating Content Performance
When other websites link to your content, it’s often a sign of its value and appeal. Analyzing these links helps in understanding the type of content that resonates with your audience, inspiring similar content creation. It also aids in identifying the audience demographics of referring sites, which can broaden your target audience scope. Additionally, maintaining relationships with these website owners can be beneficial for future content strategies.
Measuring Backlinks’ Effectiveness
Assessing the performance of backlinks is crucial for SEO. Quality backlinks not only drive referral traffic but also enhance SERP rankings, leading to increased organic traffic. Tracking the impact of backlinks through referral data helps in evaluating their contribution to your website’s success.
Summary
Referral traffic data in GA4, while challenging to dissect fully, offers valuable insights. Tracking full-page URLs of referrers, though time-consuming, can be approached through methods like event tracking, similar to Google’s merchandise store. Excluding unwanted referrals, such as third-party payment gateways and self-referrals, is crucial for accurate data analysis. Understanding and utilizing referral traffic data effectively can lead to improved content strategy, audience engagement, and SEO performance.
Engaging with your referral sources, analyzing the content they link to, and measuring the effectiveness of backlinks are key strategies to leverage referral traffic data. These practices can enhance your understanding of audience preferences and drive growth.
Finally, we encourage feedback on how you manage unwanted referrals and utilize referral traffic data. Share your experiences in the comments below for further discussion!