In the ever-evolving digital landscape, maintaining the security and integrity of your website is paramount. Google Search Console (GSC) plays a crucial role in this regard, offering webmasters a suite of tools to monitor, manage, and enhance their site’s visibility in Google search results. With Google Search Console at your disposal, identifying and resolving security threats becomes a manageable task. This article delves into the nature of “security issues” flagged by Google, their various forms, and the steps required to address them, ensuring the safety and integrity of your online presence.
Understanding Security Issues in Google Search Console
Security issues in Google Search Console refer to vulnerabilities or concerns on a website that could jeopardize its safety. Google’s sophisticated algorithms are constantly on the lookout for such issues, alerting website owners through the Search Console as soon as any threat is detected. These security problems can take many shapes, including:
- Hacked content, which involves unauthorized modifications to your website, potentially introducing harmful links, spam, or irrelevant data.
- Malware infections, where malicious software infiltrates your site, posing a risk to your visitors’ devices and personal information.
- Deceptive pages, designed to trick users into revealing sensitive data or downloading dangerous software. Google flags these to protect users from scams.
Finding and Fixing Security Issues
Navigating and effectively utilizing the Google Search Console’s Security and Manual Actions feature is crucial for maintaining the health and security of your website. This tool is instrumental in identifying issues that could potentially harm your site or its visitors and provides actionable insights to resolve them. Here’s a step-by-step guide to making the most of the Security and Manual Actions feature:
Step 1: Access Google Search Console
First, log into your Google Search Console (GSC) account. If you haven’t already, you will need to verify your website ownership within GSC to access its features.
Step 2: Locate Security & Manual Actions
Once logged in, look for the “Security & Manual Actions” section in the left-hand menu. This section is your gateway to understanding and resolving security issues and manual actions imposed by Google.
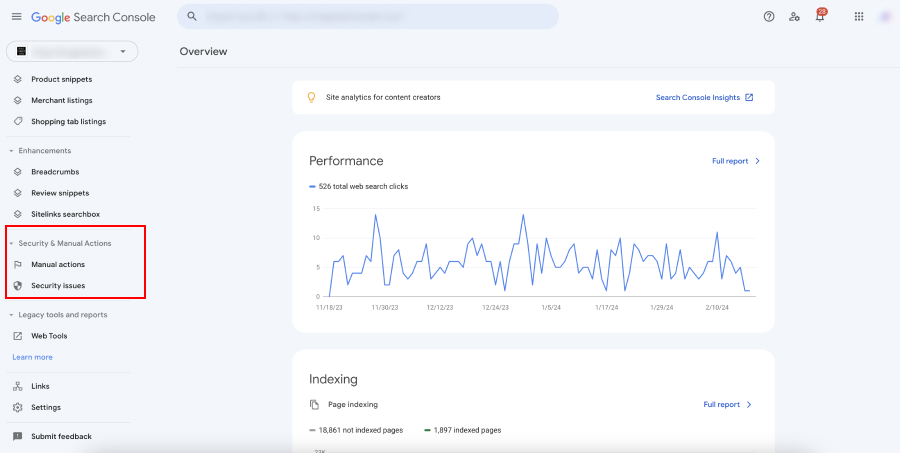
Step 3: Review Security Issues
Under “Security & Manual Actions,” click on “Security Issues.” This area will list any security issues Google has identified with your site, such as malware, hacked content, or deceptive pages. Each listed issue will include details such as the type of problem, affected URLs, and specific recommendations for resolution.
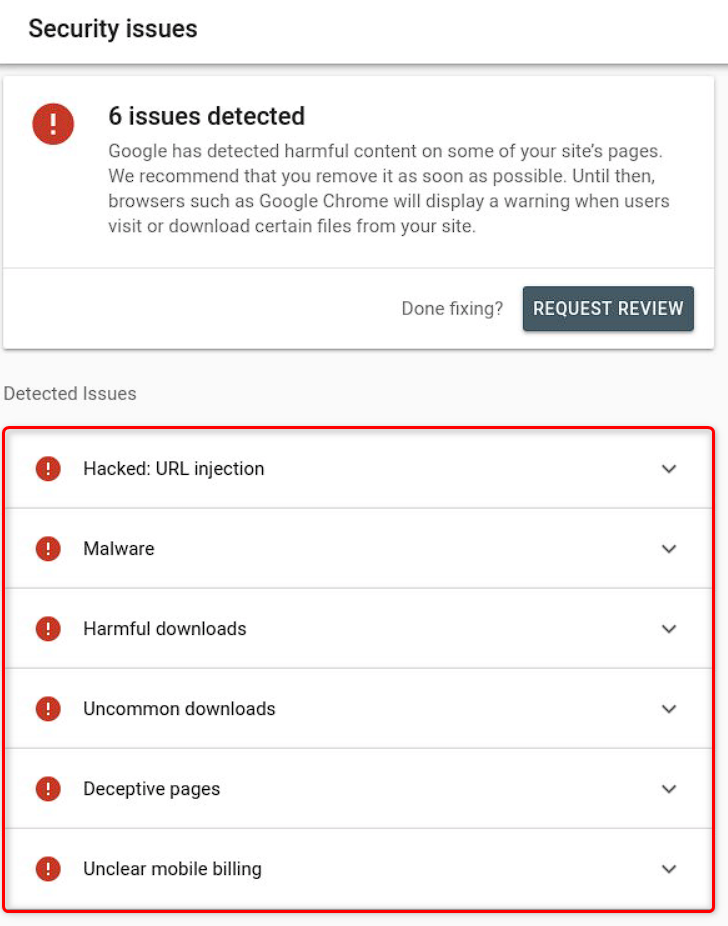
Step 4: Addressing Security Issues
Upon identifying the security issues, it’s imperative to address them promptly:
- Hacked Content: Secure your site by removing the hacked content and any backdoors that could allow hackers to regain access. Update all passwords and ensure your site’s software is up to date.
- Malware Infections: Use reputable security software to scan your site for malware. Remove any malicious code or files found and strengthen your site’s security to prevent future infections.
- Deceptive Pages: Identify and remove any pages that are designed to deceive users. Ensure your site adheres to Google’s Webmaster Guidelines to avoid being flagged for deception.
Step 5: Submitting a Review Request
After resolving the issues, return to the Security Issues section in GSC and submit a review request for each resolved issue. This tells Google that you’ve fixed the problem, prompting them to re-evaluate your site and potentially remove any security warnings associated with it.
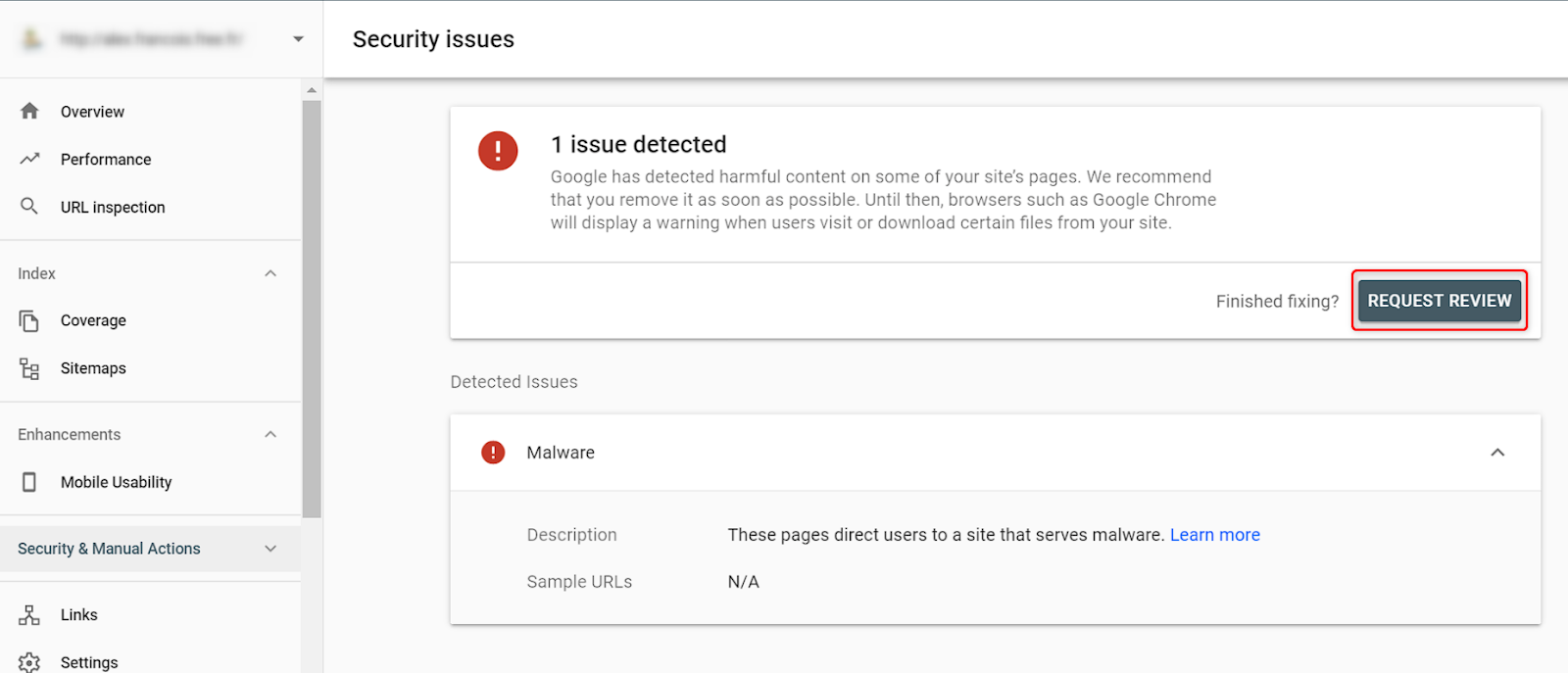
Step 6: Manual Actions
In the same “Security & Manual Actions” section, you can check if there are any manual actions against your site. These are penalties that Google applies when they detect practices that are against their guidelines. If any are listed, detailed information and steps to resolve the issue will be provided.
Step 7: Stay Proactive
Regularly check the Security Issues and Manual Actions sections, even if you haven’t received an alert from Google. Staying proactive can help you preemptively address issues before they impact your site’s ranking or reputation.
Preventative Measures
Prevention is better than cure. Here are some best practices to prevent security issues and avoid manual actions:
- Regularly update software: Keep your site’s software, including CMS and plugins, up to date to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Implement security measures: Use HTTPS, set up a web application firewall (WAF), and employ security plugins to enhance your site’s security posture.
- Follow Google’s Webmaster Guidelines: Adhere to Google’s guidelines to avoid manual actions. Focus on creating high-quality, valuable content and fostering natural link-building.
- Monitor GSC regularly: Stay vigilant by regularly checking Google Search Console for alerts and recommendations. Regular monitoring of your Google Search Console account for new security issues is vital. Staying abreast of security best practices and ensuring your website’s components are up-to-date will fortify your defenses against potential threats.
Conclusion
Google Search Console is an invaluable tool for website owners, offering the means to detect, understand, and rectify security issues. By adhering to the guidelines provided and implementing robust security measures, you can safeguard your website against various threats, ensuring a safe and secure experience for your users. Remember, the security of your website is paramount, not only for your peace of mind but also for maintaining the trust of your visitors. Moreover, it affects not only your search engine rankings but also the safety of your users. Stay informed, stay secure, and let Google Search Console be your guide in the digital wilderness.