Event tracking is a crucial aspect of using Google Analytics effectively. It helps you understand how users interact with your website beyond page views. This comprehensive guide will cover how to set up and use event tracking in both Universal Analytics (UA) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4), ensuring you can leverage this powerful feature regardless of the Analytics version you’re using.
Understanding Event Tracking
Before diving into the setup process, it’s essential to understand what event tracking is and why it’s important. In Google Analytics, an event is any interaction with your website that doesn’t involve loading a new page. This can include clicks on links, downloads, form submissions, and video plays. Tracking these events helps you gain deeper insights into user behavior and measure the effectiveness of your content and user interface.
Event Tracking in Universal Analytics
Setting up event tracking in Universal Analytics involves a few key steps:
- Decide What to Track: Identify the interactions you want to track, such as button clicks or form submissions.
- Implement Event Tracking Code: You’ll need to modify your website’s code to send event data to Google Analytics. This typically involves adding JavaScript code that uses the “ga” function to send event data.
- Verify Your Setup: After implementing the event tracking code, test it to ensure it’s working correctly. Use the Real-Time reports in Google Analytics to see if the events are being recorded as expected.
- Analyze Event Data: Once you’ve verified that events are being tracked, you can analyze the data in Google Analytics under the “Behavior” section. Look at the “Events” reports to see how users are interacting with your site.
Event Tracking in Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 offers a more streamlined approach to event tracking, with some events tracked automatically. However, you might still need to set up custom events. Here’s how to do it:
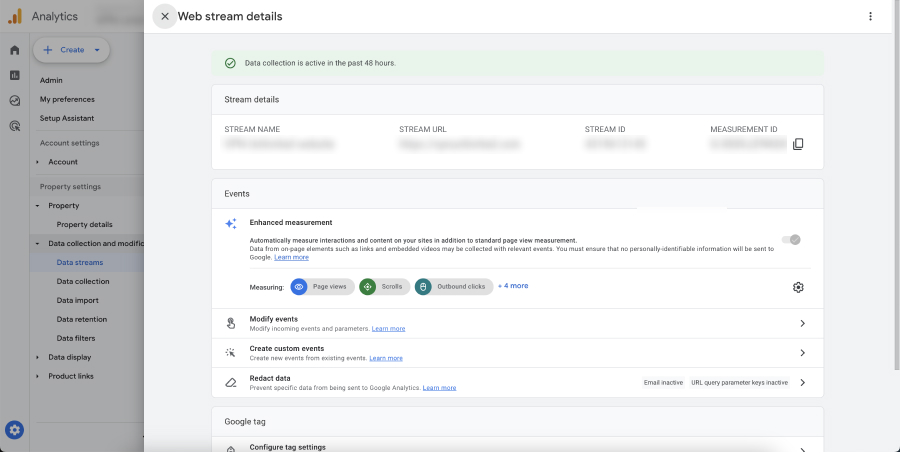
- Enable Enhanced Measurement: GA4 automatically tracks certain events through Enhanced Measurement. To enable it, go to your GA4 property, click on ‘Data Streams’, select your web stream, and turn on Enhanced Measurement.

- Use Google Tag Manager for Custom Events: For events not automatically tracked, use Google Tag Manager. Create a new tag with the appropriate trigger (e.g., button clicks), and set the tag type to ‘Google Analytics: GA4 Event’. Define your event parameters like ‘Event Name’, ‘Category’, ‘Action’, and ‘Label’.
- Publish Your Tags: Once you’ve set up your tags in Google Tag Manager, publish them to make the changes live.
- Verify and Analyze Your Events: Similar to UA, use the Real-Time report in GA4 to verify that your events are being tracked. Then, analyze the events in the “Events” report under the “Engagement” section.
Using Google Tag Manager to Track Events
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a powerful tool that simplifies the process of managing and deploying marketing tags (including tracking codes) on your website without having to modify the code. Here’s how you can use GTM to track events in Google Analytics:
1. Setting Up Google Tag Manager
- Create a GTM Account and Container: If you don’t have a GTM account, create one at tagmanager.google.com. Then, create a container for your website.
- Install GTM on Your Website: After creating your container, you’ll be given a snippet of code to add to your website’s source code. Place the GTM code immediately after the opening <head> tag and immediately after the opening <body> tag.
2. Creating Tags for Event Tracking
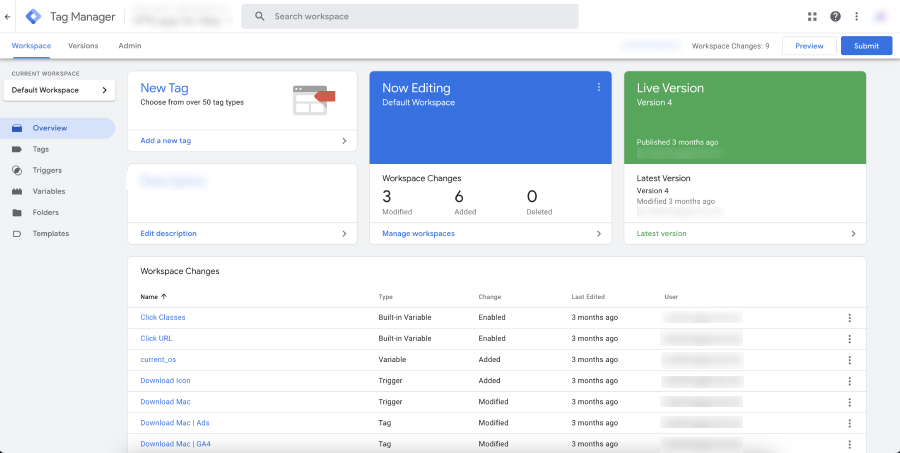
- Navigate to Your Container: In your GTM dashboard, select the appropriate container for your website.
- Create a New Tag: Click on ‘Tags’ in the left sidebar, then click ‘New’ to create a new tag.
- Configure Your Tag: Choose a tag type that corresponds to the version of Google Analytics you’re using (e.g., ‘Universal Analytics’ or ‘GA4 Event’). For Universal Analytics, you’ll also need to provide your Tracking ID.
- Set Up Event Tracking Parameters: Configure the event tracking parameters like ‘Category’, ‘Action’, and ‘Label’. For GA4, define the ‘Event Name’ and any additional parameters you want to track.
3. Defining Triggers

- Create a Trigger: Triggers tell GTM when to fire your tag. Click ‘Triggers’ in the left sidebar and then ‘New’.
- Configure Your Trigger: Select a trigger type that corresponds to the user interaction you want to track, such as ‘Click – All Elements’ for tracking all clicks, or ‘Form Submission’ for tracking form submissions.
- Set Trigger Conditions: Specify the conditions under which the trigger should fire, like clicking a specific button or link. You can use the built-in variables or create custom ones for more complex triggers.
4. Testing and Publishing Your Tags
- Preview and Debug: Before publishing your tags, use GTM’s ‘Preview’ mode to test them on your site. This mode allows you to see whether the tags fire correctly based on the defined triggers.
- Publish Your Changes: Once you’re satisfied that your tags are working correctly, go back to the GTM dashboard and click ‘Submit’ to publish your changes.
5. Verifying Event Tracking in Google Analytics
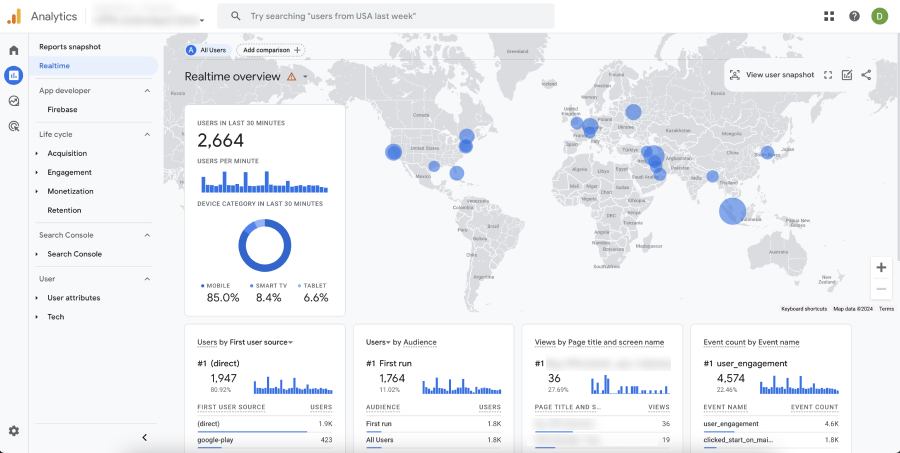
- Check Real-Time Reports: After publishing your tags, check the Real-Time reports in Google Analytics to ensure that events are being tracked as expected.
- Analyze Event Data: Analyze the events under the appropriate section in Google Analytics (e.g., ‘Events’ under ‘Behavior’ in Universal Analytics or ‘Events’ under ‘Engagement’ in GA4).
Best Practices for Event Tracking
Regardless of whether you’re using Universal Analytics or Google Analytics 4, there are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Consistent Naming Conventions: Use a consistent naming convention for event categories, actions, and labels to make analysis easier.
- Prioritize Important Events: Focus on tracking events that are most critical to understanding user behavior and achieving your business goals.
- Regularly Review and Update Event Tracking: As your website evolves, so should your event tracking setup. Regularly review and update your events to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
Conclusion
Event tracking is a powerful tool in Google Analytics that provides valuable insights into user behavior on your website. Whether you’re using Universal Analytics or Google Analytics 4, the key is to carefully plan what you want to track, implement the tracking properly, and regularly analyze the data to gain actionable insights. By following the steps and best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to make the most of event tracking in Google Analytics.